Notes
- All table interactions (References, Cochrane links, Evidence scores etc) are implemented elsewhere. Please go here to view
- Images & image captions could not be built responsively (inline in tables) as suggested in the mockups. Captions now live under the images as is the usual pattern. Please feedback.
- Icons have yet to be created / decided upon (red flag).
Snippets
Coding Standards - Please read
- Feel free to reuse the code snippets below
- All code is WCAG 2.0 Level AA compliant, valid and semantic (as of 04/2017).
- If you amend the code, please ensure that it remains thus.
Differential Diagnosis
Please note that tabs are full width on mobile (code already on dev but may need amending). Similarly, cards (white background) are full width on mobile (code already on dev). Please add logic on Dev to address hide cols / rows when no content available (i.e. Other Investigations (see mobile behaviour below))
Differential diagnosis
Common
Insomnia disorder
difficulty in initiating sleep, waking frequently, poor concentration, depressed mood
decreased alertness, red and puffy eyes, absence of physical signs suggesting organic illness
- none: diagnosis based on histry and clinical examination
Depression
difficulty in initiating sleep, waking frequently, poor concentration, depressed mood
decreased alertness, red and puffy eyes, absence of physical signs suggesting organic illness
- none: diagnosis based on histry and clinical examination
Coming soon ...
<div class="diffDiagnosis">
<h2>Differential diagnosis</h2>
<div class="card d-inline-block mb-3">
<div class="card-block p-0">
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link active" data-toggle="tab" href="#common" role="tab">Common / Uncommon</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" data-toggle="tab" href="#category" role="tab">Category</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<div class="tab-content">
<div class="tab-pane active" id="common" role="tabpanel">
<h3>Common</h3>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-block">
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="row rowHead hidden-sm-down">
<div class="col-md-3 ">History</div>
<div class="col-md-3">Exam</div>
<div class="col-md-3">1st investigation</div>
<div class="col-md-3">Other investigations</div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3><span class="material-icons text-danger" style="font-size: 1.5rem;"></span> Insomnia disorder</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-3"><span class="hidden-md-up">History</span><p>difficulty in initiating sleep, waking frequently, poor concentration, depressed mood</p></div>
<div class="col-md-3"><span class="hidden-md-up">Exam</span><p>decreased alertness, red and puffy eyes, absence of physical signs suggesting organic illness</p></div>
<div class="col-md-3"><span class="hidden-md-up">1st investigation</span><ul><li><strong>none:</strong> diagnosis based on histry and clinical examination</li></ul></div>
<div class="col-md-3"><span class="hidden-md-up">Other investigations</span> </div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3>Depression</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-3"><span class="hidden-md-up">History</span><p>difficulty in initiating sleep, waking frequently, poor concentration, depressed mood</p></div>
<div class="col-md-3"><span class="hidden-md-up">Exam</span><p>decreased alertness, red and puffy eyes, absence of physical signs suggesting organic illness</p></div>
<div class="col-md-3"><span class="hidden-md-up">1st investigation</span><ul><li><strong>none:</strong> diagnosis based on histry and clinical examination</li></ul></div>
<div class="col-md-3"><span class="hidden-md-up">Other investigations</span> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="tab-pane" id="category" role="tabpanel">
<h2>Coming soon ...</h2>
</div>
</div>
</div> <!-- /diffDiag -->Differential diagnosis
Asthma
- Onset of asthma is usually in early life. A personal or family hx of allergy, rhinitis, and eczema is often present. There is daily variability in symptoms, and patients have overt wheezing that usually rapidly responds to bronchodilators. Cough variant asthma mimics many features of COPD.
- PFTs show reversibility with bronchodilators and no decrease in diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO). Sputum or blood eosinophilia is suggestive of asthma.
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
- Patients with GORD often have dyspepsia and frequent belching, and can have a chronic cough that worsens at night when supine.
- PFTs show reversibility with bronchodilators and no decrease in diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO). Sputum or blood eosinophilia is suggestive of asthma.
Lung cancer
- Patients with GORD often have dyspepsia and frequent belching, and can have a chronic cough that worsens at night when supine.
- PFTs show reversibility with bronchodilators and no decrease in diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO). Sputum or blood eosinophilia is suggestive of asthma.
<div class="diffDiagnosis">
<h2>Differential diagnosis</h2>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-block">
<div class="container">
<div class="row rowHead hidden-sm-down">
<div class="col-md-2">Conditions</div>
<div class="col-md-5">Signs / Symptoms</div>
<div class="col-md-5">Investigations</div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-2 conTitle brdTop"><h3>Asthma</h3></div>
<div class="col-md-5"><span class="hidden-md-up">Signs / Symptoms</span> <ul><li>Onset of asthma is usually in early life. A personal or family hx of allergy, rhinitis, and eczema is often present. There is daily variability in symptoms, and patients have overt wheezing that usually rapidly responds to bronchodilators. Cough variant asthma mimics many features of COPD.</li></ul> </div>
<div class="col-md-5"><span class="hidden-md-up">Investigations</span> <ul><li>PFTs show reversibility with bronchodilators and no decrease in diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO). Sputum or blood eosinophilia is suggestive of asthma.</li></ul> </div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-2 conTitle"><h3>Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease</h3></div>
<div class="col-md-5"><span class="hidden-md-up">Signs / Symptoms</span><ul><li>Patients with GORD often have dyspepsia and frequent belching, and can have a chronic cough that worsens at night when supine.</li></ul> </div>
<div class="col-md-5"><span class="hidden-md-up">Investigations</span><ul><li>PFTs show reversibility with bronchodilators and no decrease in diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO). Sputum or blood eosinophilia is suggestive of asthma.</li></ul></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-2 conTitle"><h3>Lung cancer</h3></div>
<div class="col-md-5"><span class="hidden-md-up">Signs / Symptoms</span><ul><li>Patients with GORD often have dyspepsia and frequent belching, and can have a chronic cough that worsens at night when supine.</li></ul></div>
<div class="col-md-5"><span class="hidden-md-up">Investigations</span><ul><li>PFTs show reversibility with bronchodilators and no decrease in diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO). Sputum or blood eosinophilia is suggestive of asthma.</li></ul></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div> <!-- /diffDiag -->Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
spirometry
COPD is classified based on the patient's FEV1 and its percentage of the predicted FEV1. In cases where FVC may be hard to measure, FEV6 (forced expiratory volume at 6 seconds) can be used. [Evidence A]
FEV1/FVC ratio <0.70; total absence of reversibility is neither required nor the most typical result
CXR
Seldom diagnostic, but useful in ruling out other pathologies. [2]
Increased anteroposterior ratio, flattened diaphragm, increased intercostal spaces, and hyperlucent lungs may be seen.
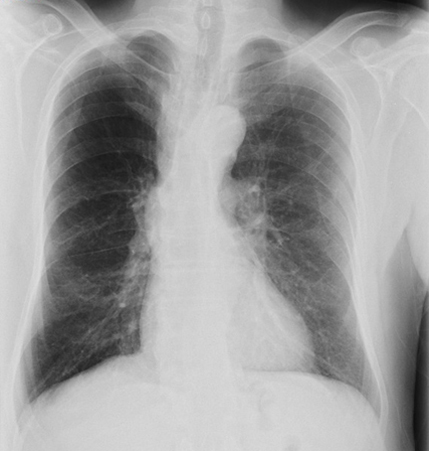
May also demonstrate complications of COPD, such as pneumonia and pneumothorax.
hyperinflation
FBR
COPD
Suspected in patients with a history of smoking, occupational/environmental risk factors, or a personal or family history of chronic lung disease. Presents with progressive shortness of breath, wheeze, cough, and sputum production. Treatment includes smoking cessation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids. Long-term oxygen therapy improves survival in severe COPD.
Acute COPD exacerbation
Acute exacerbations of COPD range from very mild to severe and life-threatening, and are commonly triggered by bacterial or viral pathogens, pollutants, or changes in temperature and humidity. They present with an acute-onset, sustained worsening of the patient's respiratory symptoms, lung function, functional status, and quality of life. [4] [5] [6]
<div class="diffDiagnosis">
<h2>Diagnostic investigations</h2>
<h3>1st investigations to order</h3>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-block">
<div class="container">
<div class="row rowHead hidden-sm-down">
<div class="col-md-8">Test</div>
<div class="col-md-4">Result</div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3>spirometry</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-8"><span class="hidden-md-up">Test</span><p>COPD is classified based on the patient's FEV1 and its percentage of the predicted FEV1. In cases where FVC may be hard to measure, FEV6 (forced expiratory volume at 6 seconds) can be used. <a href="#" class="refLink">[Evidence A]</a></p></div>
<div class="col-md-4"><span class="hidden-md-up">Result</span><p>FEV1/FVC ratio <0.70; total absence of reversibility is neither required nor the most typical result</p></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3>CXR</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-8"><span class="hidden-md-up">Test</span><p>Seldom diagnostic, but useful in ruling out other pathologies. <a href="#" class="refLink">[2]</a></p>
<p>Increased anteroposterior ratio, flattened diaphragm, increased intercostal spaces, and hyperlucent lungs may be seen.</p>
<figure class="figure">
<img src="../../../css/images/diff_diag_img.jpg" alt="chest x-ray">
<figcaption class="figure-caption">COPD chest x-ray (AP view): hyperinflated lung, flattened diaphragm, increased intercostal spaces
<span class="imgCredit">From the collection of Manoochehr Abadian Sharifabad, MD</span></figcaption>
</figure>
<p>May also demonstrate complications of COPD, such as pneumonia and pneumothorax.</p></div>
<div class="col-md-4"><span class="hidden-md-up">Result</span><p>hyperinflation</p></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3>FBR</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-8"><span class="hidden-md-up">Test</span><p>This test may be considered to assess severity of an exacerbation and may show polycythaemia (haematocrit >55%), anaemia, and leucocytosis. <a href="#" class="refLink">[49]</a> <a id="CochranePop" class="refLink" data-trigger="focus" data-toggle="popover">[<img class="cochraneInline" src="../../../css/images/cochrane-logo.svg" alt="Cochrane logo" />]</a></p></div>
<div class="col-md-4"><span class="hidden-md-up">Result</span><p>raised haematocrit, possible increased WBC count</p></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div> <!-- /diffDiag -->
<div class="diffDiagnosis">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-block">
<div class="container">
<div class="row rowHead hidden-sm-down">
<div class="col-md-4">Condition</div>
<div class="col-md-8">Description</div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-4 conTitle"><h3>COPD</h3></div>
<div class="col-md-8"><p>Suspected in patients with a history of smoking, occupational/environmental risk factors, or a personal or family history of chronic lung disease. Presents with progressive shortness of breath, wheeze, cough, and sputum production. Treatment includes smoking cessation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids. Long-term oxygen therapy improves survival in severe COPD.</p></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-4 conTitle"><h3>Acute COPD exacerbation</h3></div>
<div class="col-md-8"><p>Acute exacerbations of COPD range from very mild to severe and life-threatening, and are commonly triggered by bacterial or viral pathogens, pollutants, or changes in temperature and humidity. They present with an acute-onset, sustained worsening of the patient's respiratory symptoms, lung function, functional status, and quality of life. <a href="#" class="refLink">[4]</a> <a href="#" class="refLink">[5]</a> <a href="#" class="refLink">[6]</a></p></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div> <!-- /diffDiag -->History & examination
presence of risk factors (e.g., smoking)
The main risk factor is smoking. Other key risk factors include advancing age and genetic factors.
cough
Usually the initial symptom of COPD.
Frequently a morning cough, but becomes constant as disease progresses.
Usually productive, and sputum quality may change with exacerbations or superimposed infection
cigarette smoking
- Most important risk factor. It causes 40% to 70% of cases of COPD. [12]
- Elicits an inflammatory response and causes cilia dysfunction and oxidative injury
advanced age
- The effect of age may be related to a longer period of cigarette smoking as well as the normal age-related loss of FEV1.
<div class="histExam">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-block">
<div class="container common">
<div class="row rowHead">
<div class="col-md-12">COMMON</div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3>presence of risk factors (e.g., smoking)</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-12"><p>The main risk factor is smoking. Other key risk factors include advancing age and genetic factors.</p></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3>cough</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-12"><p>Usually the initial symptom of COPD.</p>
<p>Frequently a morning cough, but becomes constant as disease progresses.</p>
<p>Usually productive, and sputum quality may change with exacerbations or superimposed infection</p></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div> <!-- /histExam -->
<div class="histExam">
<div class="card mt-4">
<div class="card-block">
<div class="container strong">
<div class="row rowHead">
<div class="col-md-12">STRONG</div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3>cigarette smoking</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-12">
<ul>
<li>Most important risk factor. It causes 40% to 70% of cases of COPD. [12]</li>
<li>Elicits an inflammatory response and causes cilia dysfunction and oxidative injury</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><h3>advanced age</h3></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-12">
<ul>
<li>The effect of age may be related to a longer period of cigarette smoking as well as the normal age-related loss of FEV1.</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div> <!-- /histExam -->Diagnostic guidelines
Diagnostic guidelines
Published by: National Institiute for Health and Care Excellence
Last published: 2010
<div class="diagGuidelines">
<h2>Diagnostic guidelines</h2>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-block">
<div class="container">
<div class="row rowHead">
<div class="col-md-12">EUROPE</div>
</div>
<div class="row rowCondition">
<div class="col-md-12"><p><a href="#">Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management <span class="material-icons material-icons-inline">open_in_new</span></a></p></div>
</div>
<div class="row rowDetails">
<div class="col-md-12"><p><span>Published by:</span> National Institiute for Health and Care Excellence</p>
<p><span>Last published:</span> 2010</p></div>
</div>
</div><!-- /container -->
</div><!-- /card-block -->
</div><!-- /card -->
</div> <!-- /diagGuidelines --> ]
]